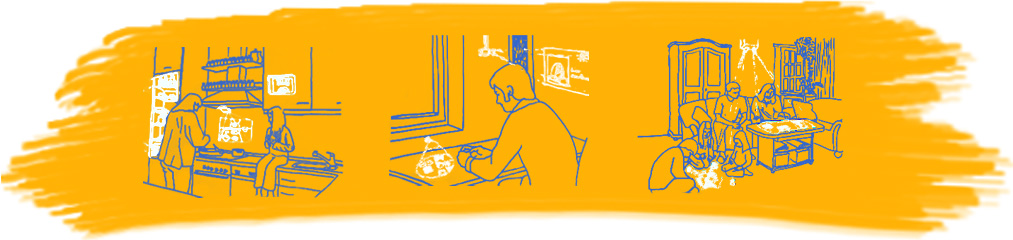
 The Fluid Beam system allows rectified and
focused projection onto arbitrary surfaces in a room. Office environments
offer multiple opportunities for projection, as parts of the furniture and
most walls are bright (often white) and plain. Thus they provide an optimal
projection surface. Using projection, the room has the ability to present
specific information about objects in it to the user. This can be done either
by text or images.
The Fluid Beam system allows rectified and
focused projection onto arbitrary surfaces in a room. Office environments
offer multiple opportunities for projection, as parts of the furniture and
most walls are bright (often white) and plain. Thus they provide an optimal
projection surface. Using projection, the room has the ability to present
specific information about objects in it to the user. This can be done either
by text or images.
In order to annotate an object, we need information about its position in the room. We therefore decribe objects by the coordinates of their bounding box. Available display surfaces are modelled as large as possible and are described by the coordinates of their corner points. They can even be defined directly onto the objects.
 A display surface can hold multiple annotations at the same time. For this
reason the original display surface is partitioned into small pieces. Now
we can tell whether such a piece is currently available or not. In the case
of a text annotation the format of the text (size or style) can be modified.
To increase the text readability we can specify a desired width-height-ratio,
for instance 2:1. So the annotation text is wrapped such that the specified
ratio is roughly achieved. Furthermore a colored border is set around the
annotation so that annotations related to the same object have a border of
the same color.
A display surface can hold multiple annotations at the same time. For this
reason the original display surface is partitioned into small pieces. Now
we can tell whether such a piece is currently available or not. In the case
of a text annotation the format of the text (size or style) can be modified.
To increase the text readability we can specify a desired width-height-ratio,
for instance 2:1. So the annotation text is wrapped such that the specified
ratio is roughly achieved. Furthermore a colored border is set around the
annotation so that annotations related to the same object have a border of
the same color.
Now the main task is to find the best display surface for the annotation. Since many potential display surfaces can exist in a room, a preselection of potential display surfaces according to the dimension of the object and the size of the annotation is done in a first step. After this preselection, the remaining ones are rated according to several criteria, such as distance to the annotated object, user position, distances to other objects and already existing annotations, and quality of the display surface. These criteria are weighted differently, so that some of them have more effect on the rating of display surfaces than others.
 The result of the rating is a ranking of display surfaces, but it doesn't
suffice just to select the best rated one because the selected position has
to fulfill two further conditions. The display surface should not be located
in a bad angle to the user since in this case an annotation could not be easily
read by the user. Furthermore there must be enough free pieces of display
surfaces in the direct neighborhood of this display surface. If these two
conditions are fulfilled the annotation is placed there and the status of
the corresponding display surfaces changes to "occupied". In case
of a deletion of this annotation at a later time the used display surfaces
are released again.
The result of the rating is a ranking of display surfaces, but it doesn't
suffice just to select the best rated one because the selected position has
to fulfill two further conditions. The display surface should not be located
in a bad angle to the user since in this case an annotation could not be easily
read by the user. Furthermore there must be enough free pieces of display
surfaces in the direct neighborhood of this display surface. If these two
conditions are fulfilled the annotation is placed there and the status of
the corresponding display surfaces changes to "occupied". In case
of a deletion of this annotation at a later time the used display surfaces
are released again.
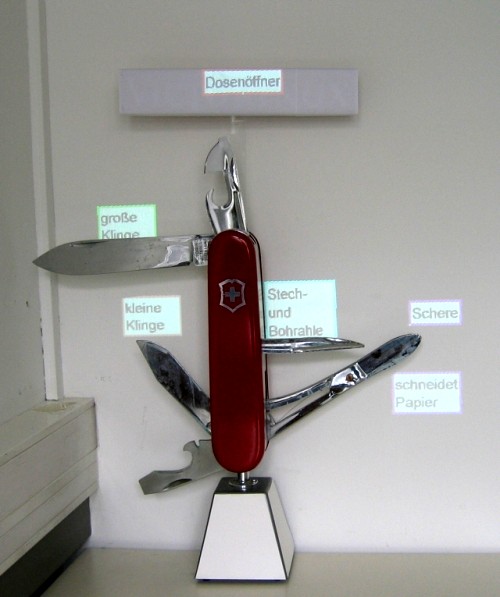
 For demonstration purposes a graphical interface was developped which allows
the annotation of a sample object (an approximately 1m tall model of a Swiss
army knife). In addition, both the weights of the criteria and the format
settings of the text can be changed. Results of created annotations are illustrated
in the images on this page.
For demonstration purposes a graphical interface was developped which allows
the annotation of a sample object (an approximately 1m tall model of a Swiss
army knife). In addition, both the weights of the criteria and the format
settings of the text can be changed. Results of created annotations are illustrated
in the images on this page.